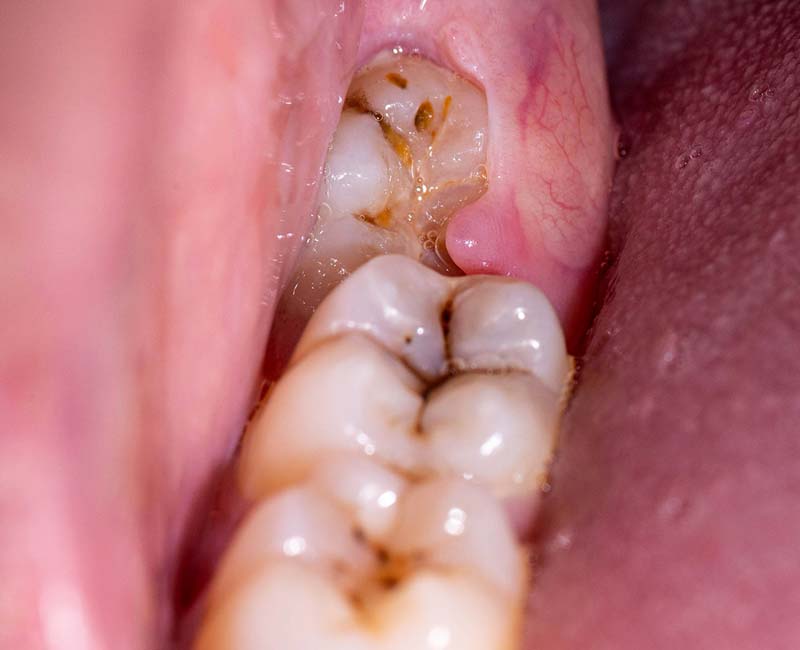
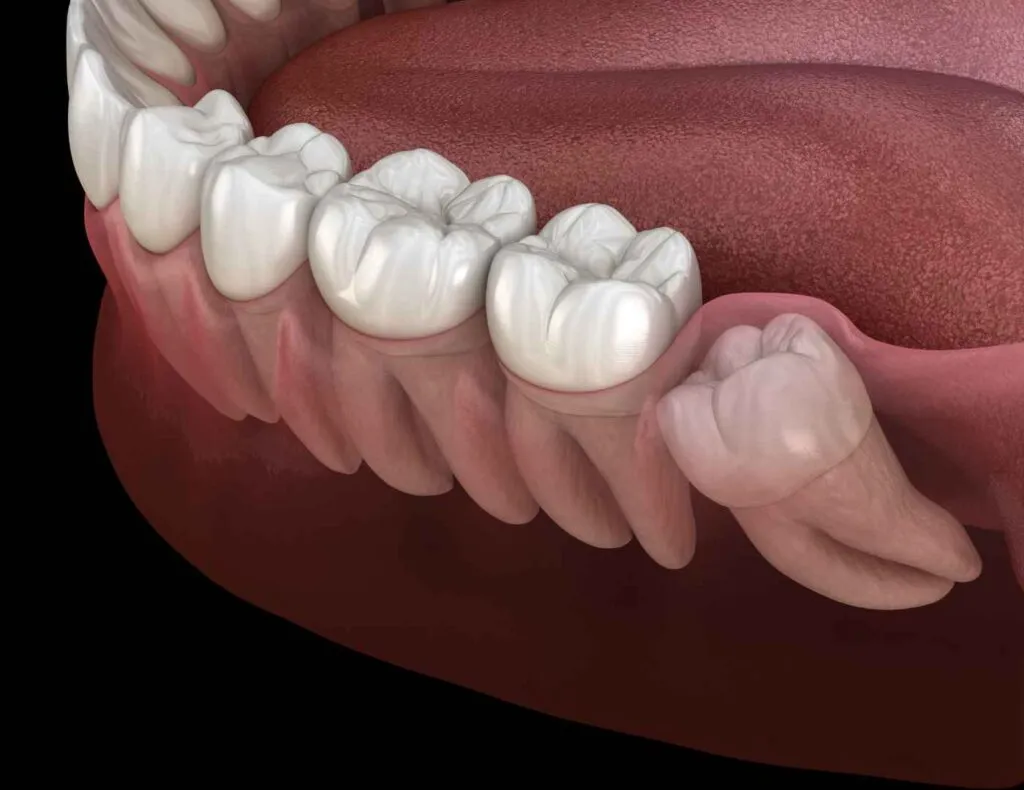
Impacted tooth extraction is a surgical procedure performed to remove a tooth that has failed to fully erupt into its normal position in the mouth.
This condition is most commonly associated with third molars (wisdom teeth), but can also affect other teeth, such as canines and premolars.
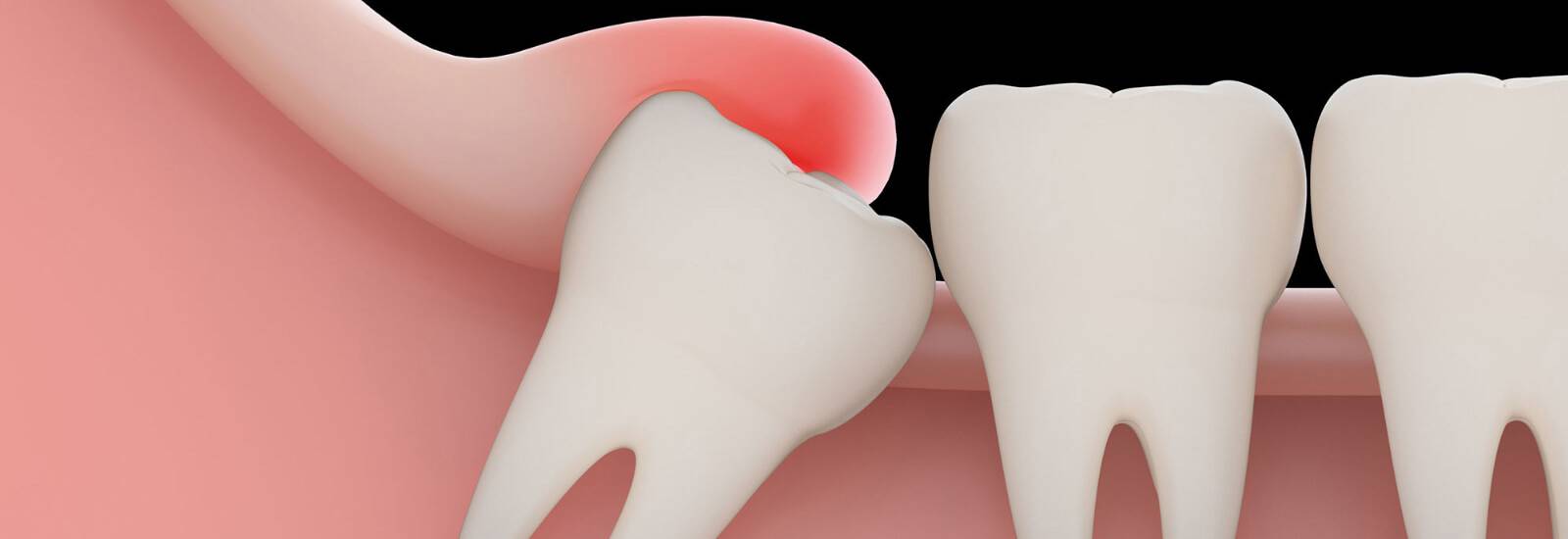
What Is an Impacted Tooth?
An impacted tooth is one that is blocked from erupting properly due to lack of space, misalignment, or obstruction by another tooth, bone, or soft tissue.
There are different types of impactions:
- Soft tissue impaction: The tooth is covered by gum tissue.
- Partial bony impaction: Part of the tooth is covered by bone.
- Complete bony impaction: The tooth is completely encased in bone.
Indications for Extraction
Impacted teeth may need to be extracted for several reasons:
- Pain or swelling
- Infection or abscess formation
- Damage to adjacent teeth
- Cyst or tumor development
- Orthodontic or prosthetic treatment planning
- Gum disease or decay in adjacent teeth
Postoperative Care
- Pain management with prescribed or over-the-counter medications.
- Cold compress to reduce swelling.
- Soft diet, good oral hygiene, and avoiding smoking or alcohol.
- Follow-up appointment to monitor healing and remove sutures if necessary.
Complications
- Swelling and bruising
- Dry socket (alveolar osteitis)
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Nerve injury (numbness or tingling)
- Sinus complications (for upper teeth)
Impacted tooth extraction is a routine but critical procedure to prevent or resolve oral health issues.
While it is generally safe and successful, careful evaluation, surgical skill, and proper aftercare are essential for optimal healing and outcomes.