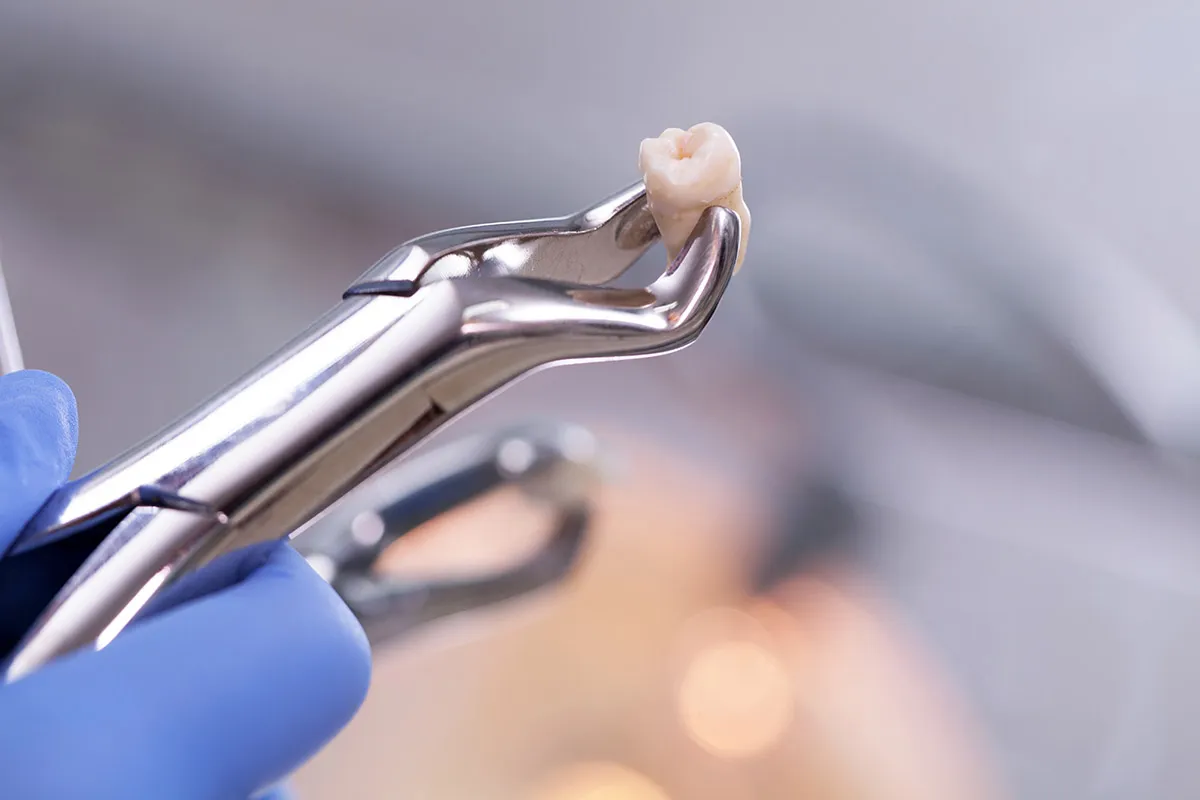
Surgical Tooth Extraction
Surgical Tooth Extraction
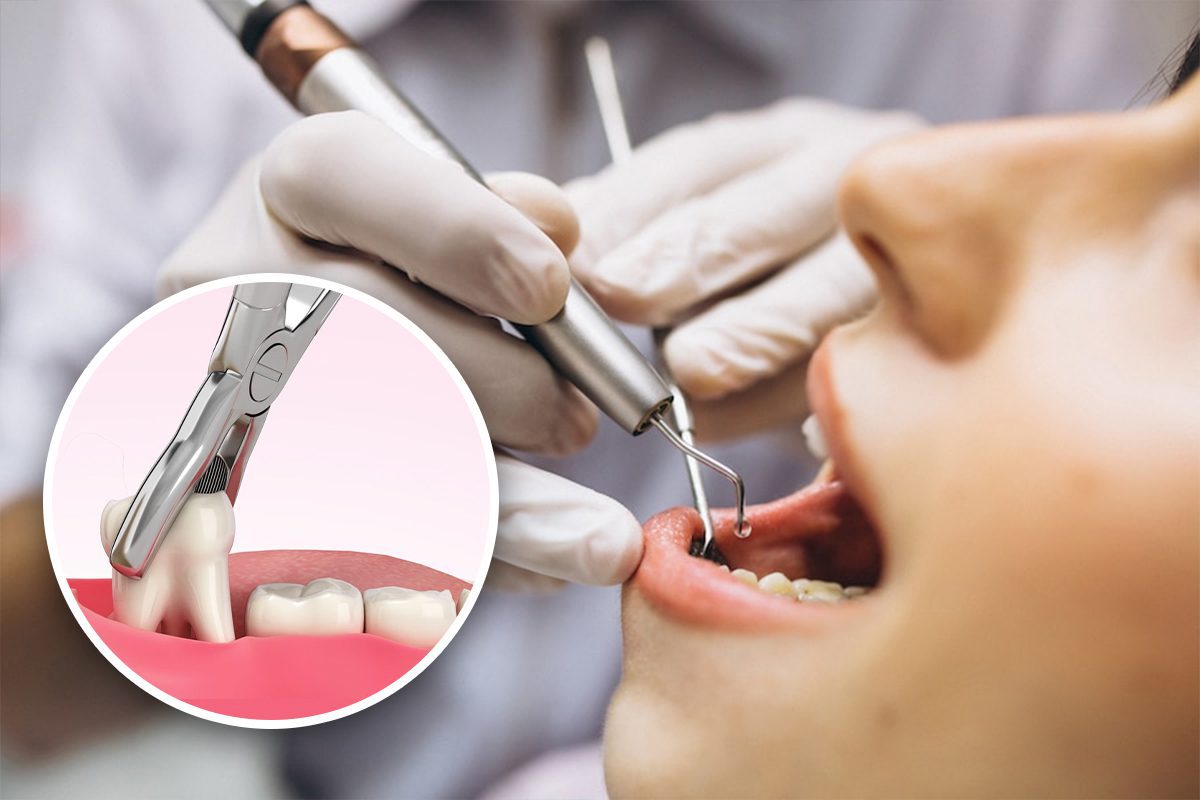
Surgical tooth extraction is a dental procedure performed to remove a tooth that cannot be easily accessed or removed by simple extraction methods.
Unlike a simple extraction, where the tooth is visible and easily removable, surgical extraction involves making an incision in the gum and sometimes removing bone or
cutting the tooth into pieces to facilitate its removal.
When is Surgical Extraction Needed?
Surgical extractions are typically required in the following cases:
- Impacted teeth: Common with wisdom teeth that do not fully erupt through the gums.
- Broken or fractured teeth: If a tooth breaks off at the gum line, it may need to be surgically extracted.
- Severely decayed teeth: When decay has destroyed much of the tooth structure, making a simple extraction difficult.
- Roots with unusual curvature or long roots that are difficult to remove.
- Teeth with surrounding bone overgrowth or cysts.
Recovery and Aftercare
- Pain management: Prescribed or over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Swelling control: Use of ice packs in the first 24–48 hours.
- Oral hygiene: Gentle rinsing with salt water after 24 hours; avoid vigorous brushing near the surgical site.
- Diet: Soft foods and adequate hydration; avoid hot, spicy, or crunchy foods initially.
- Follow-up: Stitches (if non-dissolvable) may need removal after a week.
Risks and Complications
While generally safe, surgical tooth extraction carries some risks:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Dry socket (when the blood clot dislodges from the extraction site)
- Nerve damage (rare, but possible with lower wisdom tooth extractions)
- Sinus complications (for upper molars near the sinus cavity)
Surgical tooth extraction is a common and often necessary dental procedure to address complex tooth issues.
With modern techniques and proper aftercare, most patients recover smoothly and can return to normal activities within a few days.
It's essential to follow the dentist's post-operative instructions to minimize complications and ensure optimal healing.